Table of Contents
Worked example:
Data and data source
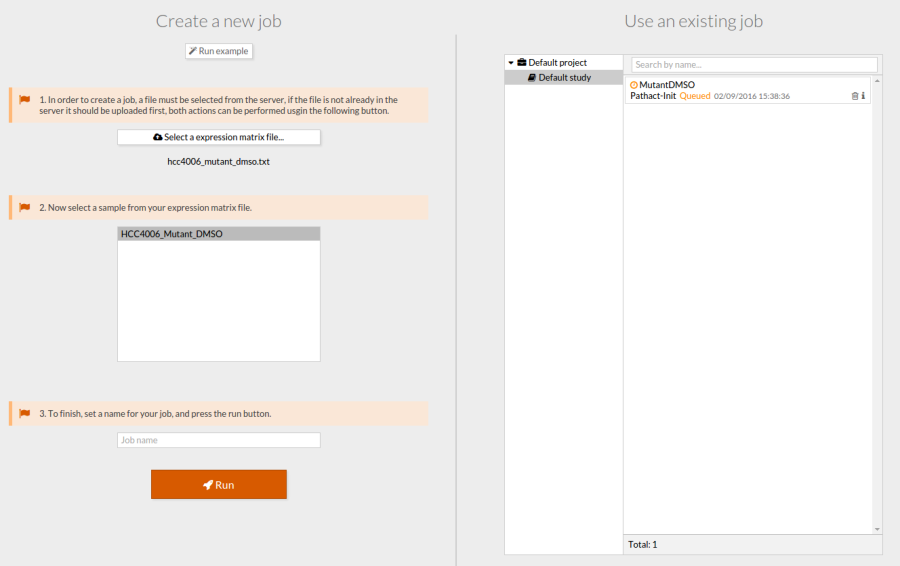
In this example we use gene expression data from NSCLC HCC4006 (EGFRm).
The file can be downloaded from this link: hcc4006_mutant_dmso.txt
And was obtained from GSE57156 project.
Steps:
- Log in PathAct using the login button on the top right corner, the login panel will appear.
- You can also login as anonymous using the start button.
- Upload the file as is shown in the Upload your data section and launch a job with that file.
- A job will appear on the right and will be processed.
- Once finished, click on it to open the view window.
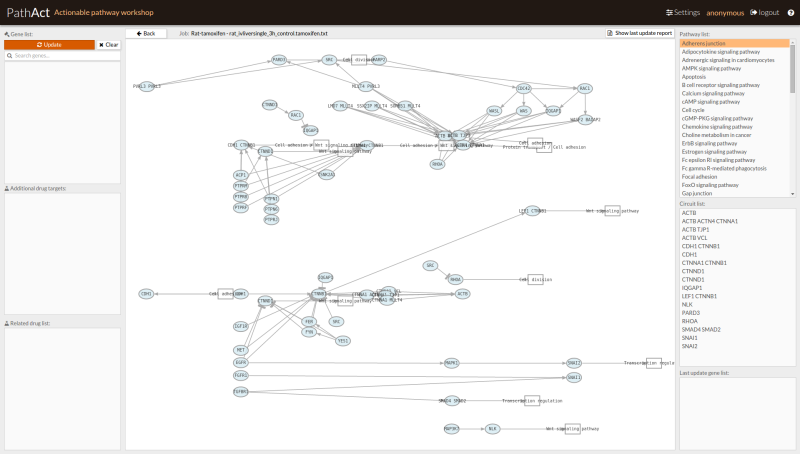
- The view window will appear.
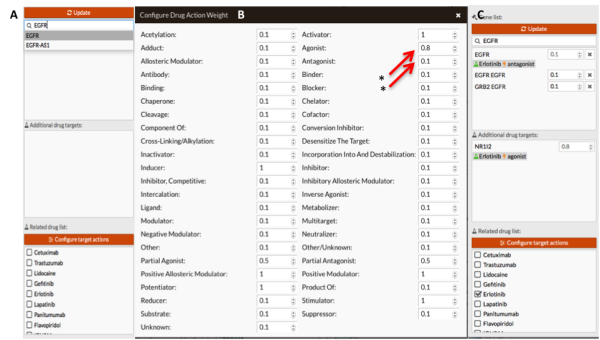
- In this example we simulate the effect of treating cells with Erlotinib (FDA approved EGFR inhibitor for treatment of NSCLC EGFR mutant). We modify the target actions fixing: Agonist = 0.8 and Antagonist = 0.1 (mechanisms of action of Erlotinib on its targets). Figure 1 shows how modify the expression of those genes using the setting panel.
- To open the settings panel click on the Settings button located at the top right corner.
Figure 1: Gene signal modification. A: Screenshot of gene selection panel. Note how the drug list appears when we select any gene. B: We modify the effect of drug action on its targets (in our case, agonist and antagonist, mark with red arrow and stars). C: Screenshot of gene selection panel after In Silico treatment with erlotinib. We have had to manually modify the expression of “EGFR - EGFR node” and “GRB2 EGFR node” because the drug annotations doesn't contain those targets.
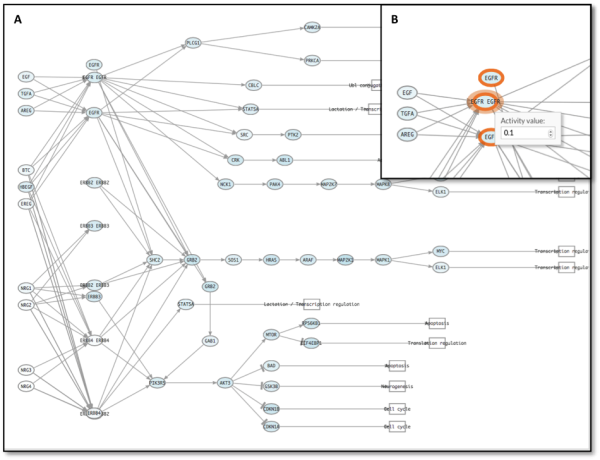
The visualizer highlights modified genes to help locate them (figure 2).
Figure 2: A: ErbB signaling pathway. B: Detail of EGFR modification on the pathway. Note how the visualizer marks perturbed genes.
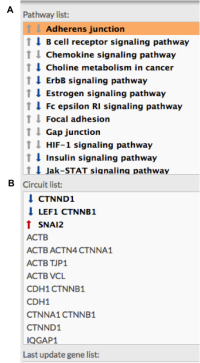
- Perform the inhibition by pressing update button. Those pathways and circuits that have been modified are marked in bold. Red or blue arrows indicate if those changes are or not significant (overactivated path or repressed).
Figure 3: Pathway list aspect after perturbation. The panel marks those pathways (A) and circuits (B) which activation has been modified (bold). Significant modification is marked with red upwards arrows (over activity) and blue down arrows (repression).
Pathways appear painted with red or blue connecting lines in the visualizer. In our example all lines are blue because our inhibition reduce the active level of all the circuit (figure 4). We show how EGFR inhibition ends in alteration of transcriptional programs that in our example stop cell growth.
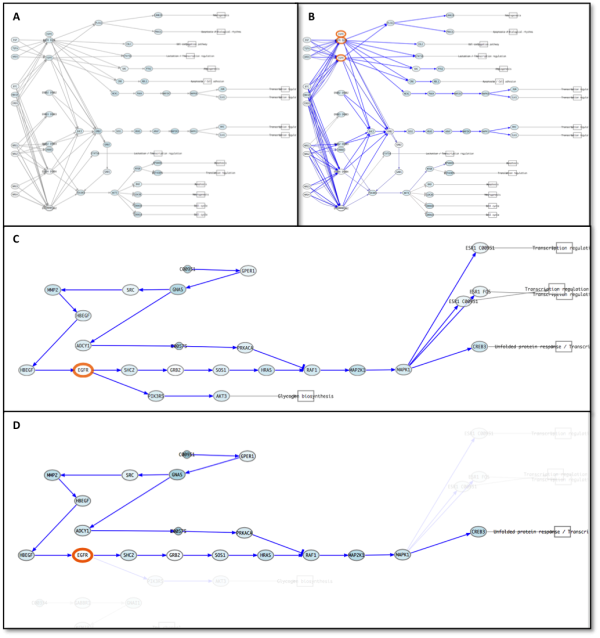
Figure 4: ErbB signaling pathway previous the perturbation (A) and after (B). Significant repressed circuits are painted in blue. C: Detail of Estrogen signaling pathway. D: CREB3 circuit of Estrogen signaling pathway. Note how the circuit selection helps to visualize correctly the perturbed system.
- PathAct allows step by step perturbations. In our example we show Erlotinib resistance acquisition by a typical way, PTEN loss and constitutive activation of HER2 (ERBB2). Figure 5 shows how system respond to alteration. The visualization of different paths remains simple and is showed in figures 6 and 7. Furthermore, circuit selection simplify user how the signal are propagated.
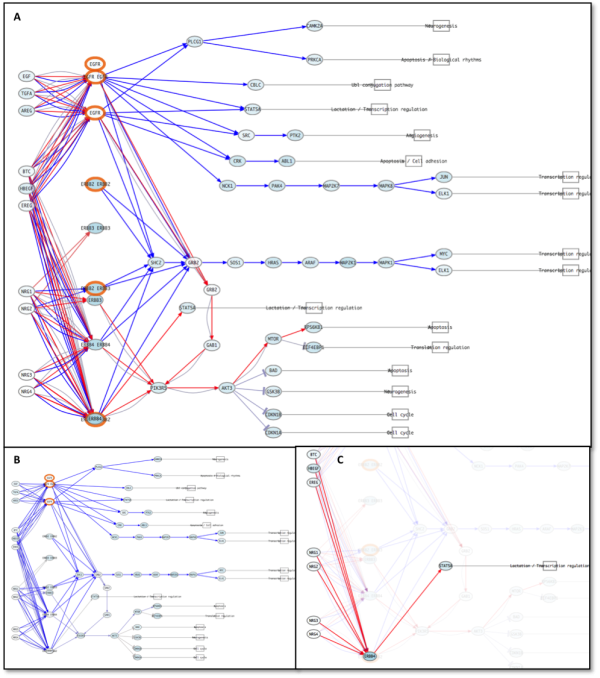
Figure 5: ErbB signaling pathway after the treatment with Erlotinib (A) and after adaptation (PTEN loss and HER2 activating mutation - B).
Figure 6: A: ErbB signaling pathway after the resistance acquisition to the treatment and previously (B). C: SAT5A circuit of ErbB signaling pathway. Note how by circuit visualization helps the interpretation.
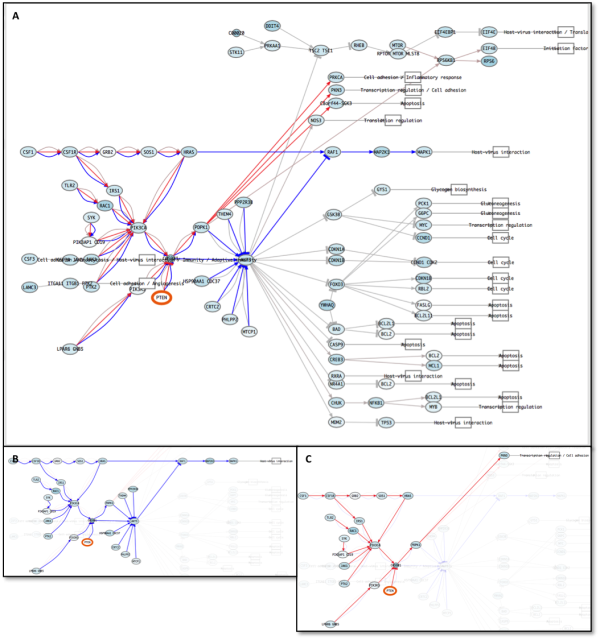
Figure 7: A: PI3K - Akt signaling pathway after second perturbation (resistance acquired to EGFR inhibitor). B: MAPK1 circuit of PI3K - Akt signaling pathway. Note how MAPK circuits are repressed and mTOR circuits are activated. C: C8orf44-SGK3 circuit of PI3K - Akt signaling pathway. Note how by circuit visualization helps the interpretation.
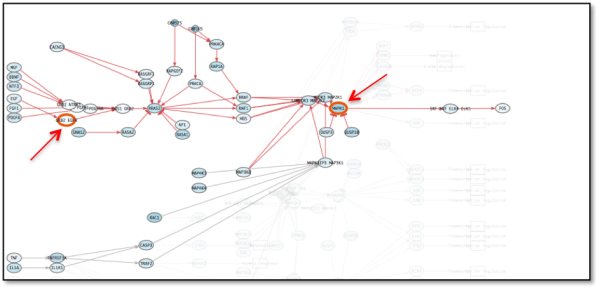
- Activating ERK mutations constitutes another important mechanism of resistance to EGFR inhibitors. Figure 8 shows how constant activation of ERK (MAPK1) offset EGFR inhibition and MAPK pathway is restored.
Figure 8: A: MAPK signaling pathway after second perturbation (resistance acquired to EGFR inhibitor by ERK activating mutation). Note how the circuit remains activated although EGFR remains inhibited.
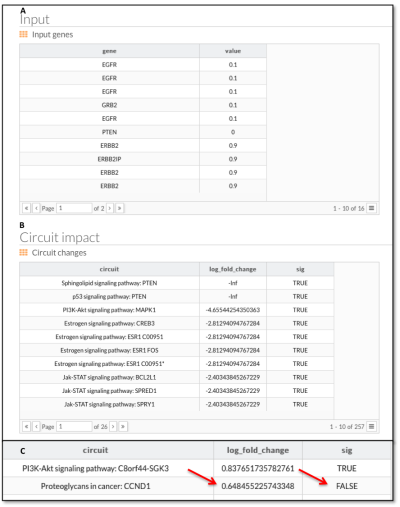
- Finally, PathAct reports (figure 9) all the gene signal alterations and circuits log fold change, discriminating between significant or not (absolute FC > 2).
Figure 9: PathAct report. A: list of perturbed genes and final value of activation. B: ranked circuits by log fold change (base 10). Note how PTEN logFC are -Infinite (PTEN loss represents a complete depletion of PTEN - complete node inactivation). C: Fold change is used by calculate significance using 2 as threshold (loge2 = 0.6931472).